Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
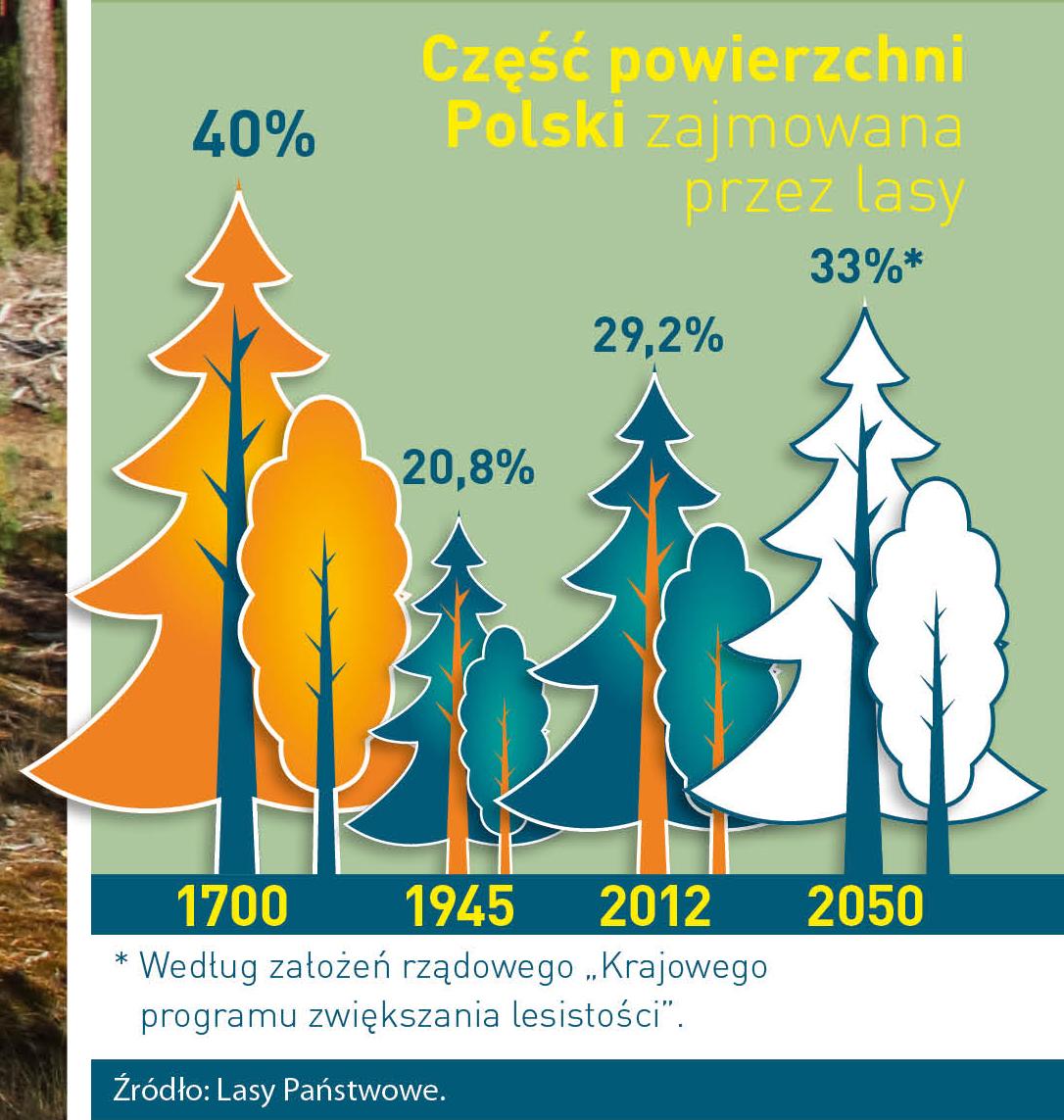
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Obszary chronionego krajobrazu
Obszary chronionego krajobrazu
Obszary chronionego krajobrazu
OBSZARY CHRONIONEGO KRAJOBRAZU
Nadleśnictwo Pomorze położone jest w zasięgu dwóch obszarów chronionego krajobrazu, które w granicach nadleśnictwa występują na powierzchni 21958,50 ha (obejmując 6340,34 ha gruntów nadleśnictwa).
Obszar Chronionego Krajobrazu ,,Pojezierze Sejneńskie"
Rozległy obszar utworzony został w dniu 2 maja 1991 r. rozporządzeniem Wojewody Suwalskiego ze zmianami zawartymi w Uchwale Nr XII/94/15 Sejmiku Województwa Podlaskiego z dnia 22 czerwca 2015 r. w sprawie Obszaru Chronionego Krajobrazu "Pojezierze Sejneńskie" (Dz. Urz. Woj. Podl. z 2015 r. poz. 2122) zm. Uchwałą Nr L/469/18 Sejmiku Województwa Podlaskiego z dnia 25 czerwca 2018 r. zmieniającą uchwałę w sprawie Obszaru Chronionego Krajobrazu "Pojezierze Sejneńskie" (Dz. Urz. Woj. Podl. z 29.06.2018 r. poz. 2907).
Łączna powierzchnia obszaru wynosi 35 981,11ha ( na terenie nadleśnictwa znajduje się 5025,69 ha).
Obejmuje tereny na wschód od Wigierskiego Parku Narodowego po granicę z Litwą. Na południu przylega do Puszczy Augustowskiej, a na północy wąskim pasem dochodzi do granicy państwa za miejscowością Puńsk. Charakteryzuje się krajobrazem o urozmaiconej rzeźbie terenu z licznymi wzniesieniami, jeziorami i rzekami oraz z cennymi przyrodniczo kompleksami leśnymi i torfowiskowymi. Czynna ochrona ekosystemów Obszaru polega na zachowaniu różnorodności biologicznej siedlisk przyrodniczych związanych z urozmaiconą rzeźbą polodowcową Pojezierza Sejneńskiego, z licznymi jeziorami, kemami, ozami i wzgórzami morenowymi.
Obszar chronionego krajobrazu ,,Puszcza i Jeziora Augustowskie"
Obszar ten został powołany przez Wojewodę Suwalskiego rozporządzeniem nr 6/91 z dnia 2 maja 1991 r. w sprawie zasad gospodarki przestrzennej na obszarach chronionego krajobrazu województwa suwalskiego. Aktualnie obowiązującym jest uchwała Nr XII/89/15 Sejmiku Województwa Podlaskiego z dnia 22 czerwca 2015 r. w sprawie Obszaru Chronionego Krajobrazu "Puszcza i Jeziora Augustowskie" wraz z późniejszymi zmianami.
Łączna powierzchnia zajmowana przez obszar wynosi 69 574,99 ha. Na terenie Nadleśnictwa Pomorze znajduje się 1314,65 ha
Obszar ten jest położony w województwie podlaskim, powiecie augustowskim na terenie gmin: Augustów, Augustów miasto, Nowinka, Płaska, Lipsk i Sztabin, w powiecie sejneńskim na terenie gminy Giby i w powiecie suwalskim na terenie gminy Suwałki i obejmuje obszar Puszczy Augustowskiej i Kanału Augustowskiego. Czynna ochrona ekosystemów Obszaru polega na zachowaniu różnorodności biologicznej siedlisk przyrodniczych kompleksu leśnego Puszczy Augustowskiej. Obszar ten należy do jednego z najbardziej atrakcyjnych turystycznie regionów Polski. Tu przebiegają prawie wszystkie szlaki kajakowe Suwalszczyzny – rzekami Rospudą, Czarną Hańczą, Blizną i Marychą. Dostępny kajakarzom jest również wybudowany w latach 1824 – 1839 Kanał Augustowski – zabytek architektury wodnej, słynny w Europie.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański